Magnetic effects of electric current mean a current-carrying wire behaves like a magnet
MAGNETIC FIELD:
The The region
surrounding a magnet, in which the force of the magnet can be exerted, is called magnetic field
ii)Magnetic field is a vector quantity that has both direction and magnitude
FIELD LINES:

The magnetic field lines start from north pole
and end at
the south pole of magnet
ii)Inside the magnet, the direction of field lines is from its south
pole to its
north pole
MAGNETIC FIELD DUE TO A CURRENT-CARRYING
CONDUCTOR:
When electric current passed in
metallic conductor produces a magnetic field around it
Magnetic Field due to a Current through a Straight
Conductor: 

The magnetic field produced
by a current-carrying straight wire is
i) directly proportional to the current passing in
wire
ii)inversely proportional to the distance of the point from the wire
Right-Hand Thumb Rule: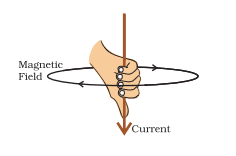
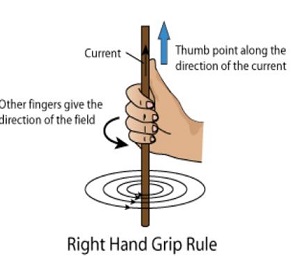
Imagine we are holding a
current-carrying straight
conductor in our right hand such that the thumb points towards
the direction of current. Then your fingers will wrap around the
conductor in the direction of the field lines of the magnetic field, This is known as the
right-hand thumb rule
Magnetic Field due to a Current through a
Circular Loop: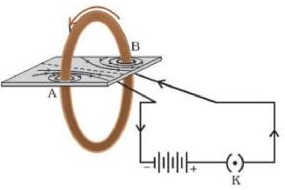

The right-hand thumb rule can be used
for a circular conducting wire . every point of a current-carrying
circular loop, the concentric circles representing the magnetic
field around. At the centre of circular wire,field lines become straight and perpendicular to
the plane of coil.
Magnetic Field due to a Current in a Solenoid:

A coil of many circular turns
of insulated copper wire wrapped
closely in the shape of a cylinder is called a solenoid.
ii)A strong magnetic field produced
inside a solenoid can be
used to magnetise a piece of magnetic material, like soft iron,
when placed inside the coil .The magnet so formed is
called an electromagnet
FORCE ON A CURRENT-CARRYING CONDUCTOR IN A MAGNETIC FIELD:
Andre Marie Ampere’s experiment:

When an current- carring conductor is placed in a magnetic field, it experiences a force. This
force is
i) directly proportional to the perpendicular direction of current
ii) directly
proportional to the perpendicular to its length and magnetic field.

stretch the thumb, forefinger and middle finger of your left hand such that they are mutually perpendicular If the first finger in the direction of magnetic field and the second finger in the direction of current, and the thumb will point in the force acting on the conductor
ELECTRIC MOTOR:
An electric motor is a rotating device that
converts electrical energy to
mechanical energy.
Principle:
when a rectangular coil is placed in a magnetic field
and current is passed through it, a force acts on the coil which rotates it continuously.
Construction: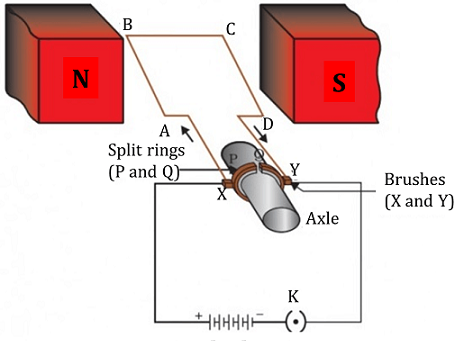
An electric motor,
consists of a rectangular
coil ABCD of insulated copper wire. The coil is placed between the two
poles of a magnetic field such that the arm AB and CD are perpendicular
to the direction of the magnetic field. The
ends of the coil are connected to the two
halves P and Q of a split ring. The inner sides
of these halves are insulated and attached
to an axle. The external conducting edges of
P and Q touch two conducting stationary
brushes X and Y, respectively,
Working: Current in the coil ABCD enters from the source battery through conducting brush X and flows back to the battery through brush Y. the current in arm AB of the coil flows from A to B. In arm CD it flows from C to D, that is, opposite to the direction of current through arm AB. On applying Fleming’s left hand rule for the direction of force on a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field the force acting on arm AB pushes it downwards while the force acting on arm CD pushes it upwards and it rotate anti-clockwise. At half rotation, Q makes contact with the brush X and P with brush Y. the current in the coil gets reversed and flows along the path DCBA. The reversal of current also reverses the direction of force acting on the two arms AB and CD. so it pushed down. Therefore the coil and the axle rotate half a turn more in the same direction. The reversing of the current is repeated at each half rotation, giving rise to a continuous rotation of the coil and to the axle
Power Source: A simple motor usually has a DC power source. It
supplies power to the motor armature or field coils.
Commutator: A device that
reverses the direction of flow of current through a circuit is called a
commutator.
Field Magnet The magnetic field helps to produce a torque on the
rotating armature coil by virtue of Fleming’s left-hand rule.
The commercial motors use:(i) an electromagnet in place of permanent
magnet;
(ii) large number of turns of the conducting wire in the currentcarrying coil;
(iii) a soft iron core on which the coil is wound.
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION:
Faraday’s experiment:
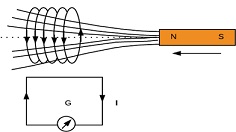
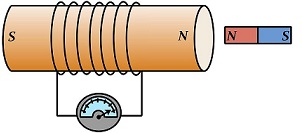
Faraday discovered that a magnetic field communicat with an electric circuit by inducing a
voltage known a electromotive force by electromagnetic induction.
When a strong bar magnet is
moved toward the coil the galvanometer show deflection
Electromagnetic induction:The phenomenon of production induced EMF due to change in magnetic field with close circuit
Fleming’s right-hand rule:
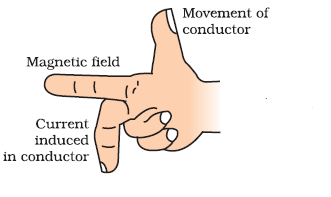
If we stretch the thumb, forefinger and middle
finger of the right hand mutually perpendicular to each other and If the thumb indicates the
direction of the movement of conductor, fore-finger indicating direction of the magnetic field,
then the middle finger indicates direction of the induced curren
ELECTRIC GENERATOR:
A generator converts mechanical energy into
electrical energy
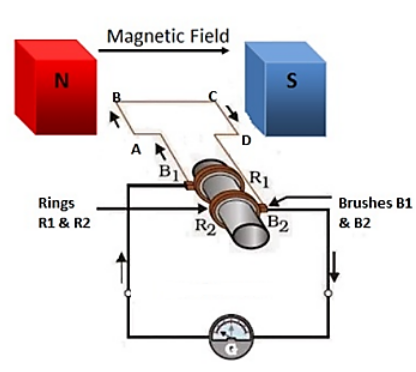
Principle:It is base on principle of electromagnetic induction such that when a straight conductor is moved in a magnetic field then currentis induced in conductor
Constuction: An electric generator consists of a rotating rectangular coil ABCD placed between the two poles of a permanent magnet. The two ends of this coil are connected to the two rings R1 and R2. The inner side of these rings are made insulated. The two conducting stationary brushes B1 and B2 are kept pressed separately on the rings R1 and R2, respectively. The two rings R1 and R2 are internally attached to an axle. The axle may be mechanically rotated from outside to rotate the coil inside the magnetic field. Outer ends of the two brushes are connected to the galvanometer to show the flow of current in the given external circuit.Working: The rotating the loop in a magnetic field, the side AB moves upward and the side CD moves downwards respectively in the produced magnetic field. Thus, current is induced in it whose direction can be determined by Flemings right hand rule. After half rotation, the ring P comes in contact with brush Y and the ring Q, comes in contact with brush X. Thus, the brush X is always in contact with the side moving upwards and brush Y is always in contact with side moving downwards as a result of which the current flows in one direction. This current is called direct current. This type of generator is called D.C. generator. Similarly, instead of a half ring, if a full ring is used then, A.C. current can be generated and such a generator is called an A.C. generator.
Note: The difference between the direct and alternating currents is that the direct current always flows in one direction, whereas the alternating current reverses its direction periodically.
DOMESTIC ELECTRIC CIRCUITS:

ii)Earth wire has a voltage of 0V and is covered with green insulation
Electric Fuse 
i) Overloading can occur when
the live wire and the neutral wire come into direct contact. This
occurs when the insulation of wires is damaged or there is a fault in the appliance
ii)The use of an electric fuse
prevents the electric circuit and the appliance from a possible damage
by stopping the flow of unduly high electric current
iii) overloading the current in circuit increases and becomes hazardous. Joule’s heating in the
fuse device melts the circuit and breaks the flow of current in the circuit
iv)Fuse work as protective device in an electrical circuit in times of overloading. when we too
many appliances of high power rating are used at the same time