Quick actions
Stay organised
Bookmark tricky proofs or add doubts to your dashboard so they resurface before exams.
Open dashboard →NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 11 – Constructions
Master "Constructions" with step-by-step NCERT solutions.
Exercise 11.1
Question 1
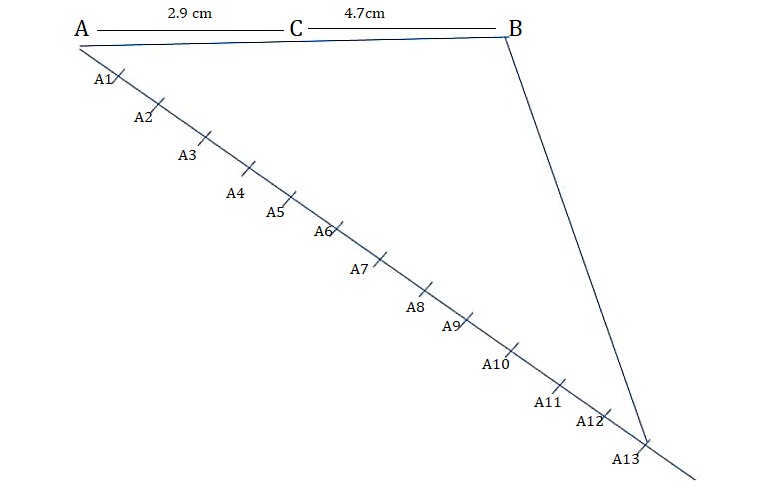
Draw a line segment of length 7.6 cm and divide it in the ratio 5 : 8. Measure the two partsAnswer
Step 1:Draw line AB of 7.6cm
Step 2:Draw a line AX with angle BAX
Step 3:Mark point A1,A2,A3,A4............A13 On AX such that AA1 = A1A2 = A2A3
Step 4:Join a line B and A13
Step 5:Draw a parallel line A5 to BA13 abd makes an angle ∠AA13B ,join a C
Step 6:now AP :PB = 5:8 and AP=2.9cm ,PB=4.7cm
Justification:
By construction, we have CA5 || B13 .
AC/CB =AA5/AA5AA13 = 5/8
AC/CB = 5/ 8
Question 2
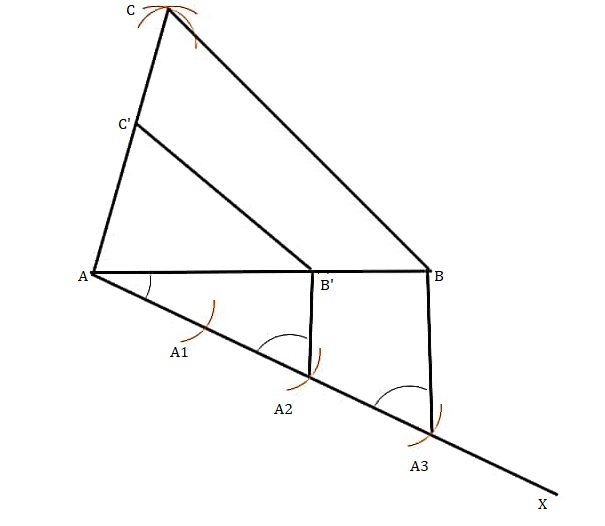
Construct a triangle of sides 4 cm, 5 cm and 6 cm and then a triangle similar to it whose sides are 2/3 of the corresponding sides of the first triangle.Answer
Step 1: Draw a line AB of 4 cm
Step 2: Using a point A draw an arc of radius 5 cm
Step 3: Similarly, Using a point B as its centre, and draw an arc of radius 6 cm.
Step 4: Now join C to A and B and form ΔABC triangle.
Step 5:Draw a line AX with angle BAX
Step 6: Make 3 points such as A1, A2, A3 on line AX such that AA1= A1A2 = A2A3.
Step 8: Join the BA3 through A2 which is parallel to the line BA3 meeting AB at point B’.
Step 9: Using point B’, draw a line parallel to the line BC meeting AC at C’.
Justification:
Here
AB’ = (2/3)AB
B’C’ = (2/3)BC
AC’= (2/3)AC
By construction we get B’C’ || BC
∴ ∠AB’C’ = ∠ABC (Corresponding angles)
In ΔAB’C’ and ΔABC,
∠ABC = ∠AB’C (Proved above)
∠BAC = ∠B’AC’ (Common)
∴ ΔAB’C’ ∼ ΔABC (by AA similarity )
So AB’/AB = B’C’/BC= AC’/AC …. (1)
In ΔAAB’ and ΔAAB,
∠A2AB’ =∠A3AB (Common)
∠AA2B’ =∠AA3B (Corresponding angles)
∴ ΔAAB’ ∼ ΔAAB (by AA similarity )
AA2B’ and AA3B
So, AB’/AB = AA2/AA3
AB’/AB = 2/3 ……. (2)
From the eq (1) and (2)
AB’/AB=B’C’/BC = AC’/ AC = 2/3
AB’ = (2/3)AB
B’C’ = (2/3)BC
AC’= (2/3)AC
Question 3
Construct a triangle with sides 5 cm, 6 cm and 7 cm and then another triangle whose sides are 7/5 of the corresponding sides of the first triangleAnswer
Construction Step
Step 1: Draw a line AB =5 cm.
Step 2: Take point A and B as centre, and draw the arcs of radius 6 cm and 5 cm and join at C.
Step 3: Draw a line AX with angle BAX
Step 5: Mark 7 points such as A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7 , on line AX such that AA1 = A1A2 = A2A3 = A3A4 = A4A5 = A5A6 = A6A7
Step 6: Join the points B to A5
Step 7: A7B' is draw a parallel to A5B.
Step 8: Now,from B’ draw a line with point C’ that is parallel to the line BC.
Step 9: ΔAB’C’ is the triangle.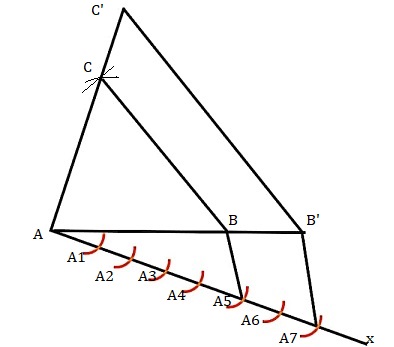
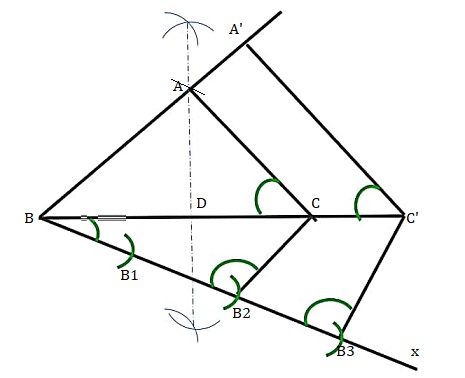
Question 4
Construct an isosceles triangle whose base is 8 cm and altitude 4 cm and then another triangle whose sides are 1Answer
Step 1: Draw a line of 8cm
Step 2:Make a perpendicular bisector of BC' at point D
Step 3: D as center deaw a arc of 4 cm intersect the perpendicular bisector at the point A
Step 4:meeting AB and AC
Step 5:Draw a line BX with angle line BC
Step 6:Mark 3 points B1, B2 and B3 on the line BX such that BB1 = B1B2 = B2B3
Step 7:Join the points B2C and draw a line from B3 parallel to the line B2C,to intersects the extended line BC at point C’.
Step 8:Draw a line from C’ parallel to the line AC to intersect extended line AB at A’
Question 5
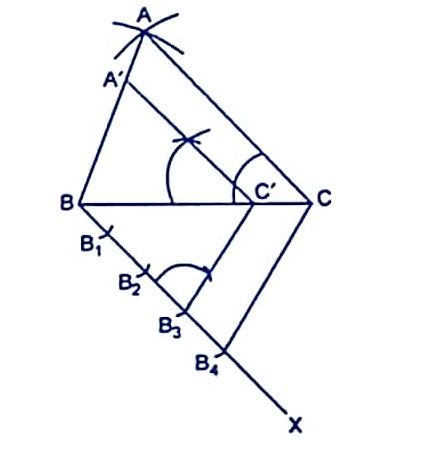
Draw a triangle ABC with side BC = 6 cm, AB = 5 cm and ∠ABC = 60°. Then construct a triangle whose sides areAnswer
Step 1:Draw a line BC = 6 cm,
Step 2:At point B draw ∠ABC = 60°.
Step 3: B as center make arc of 5cm and mark point A
Step 4:Join AB and AC
Step 5: Draw a line BX makes an acute angle with BC
Step 6:Mark 4 points such as B1, B2, B3, B4, on line BX.
Step 7:Join the points B4C ,draw a line through B3, parallel to B4C intersecting the line BC at C’
Step 8: From C’ draw a line that is parallel to the line AC and intersects the line AB at A’.
Question 6
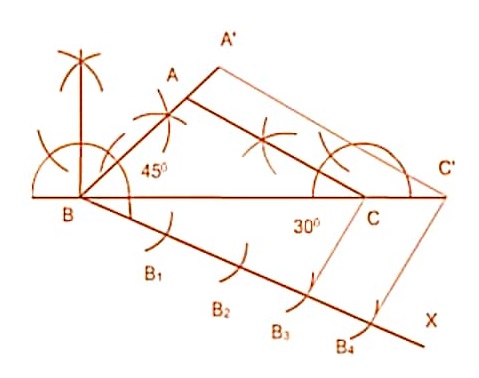
Draw a triangle ABC with side BC = 7 cm, ∠B = 45°, ∠A = 105°. Then, construct a triangle whose sides areAnswer
∠B = 45°, ∠A = 105°
We know that
Sum of angles in a triangle is 180°.
∠A+∠B +∠C = 180°
105°+45°+∠C = 180°
∠C = 180° − 150°
∠C = 30°
Step 1:Draw a line BC = 7 cm
Step 2:Draw ∠B =45 and ∠C =30
Step 3:Make a point A and join AB and AC
Step 4: Draw a line BX with acute angle with BC
Step 5: Mark 4 points such as B1, B2, B3, B4, on the ray BX.
Step 6: Join the points B3C
Step 7: from B4 draw a line parallel to B3C to intersects extended line BC at C’.
Step 8: From C’, draw a line parallel to the line AC to intersects extended line at C’.
Question 7
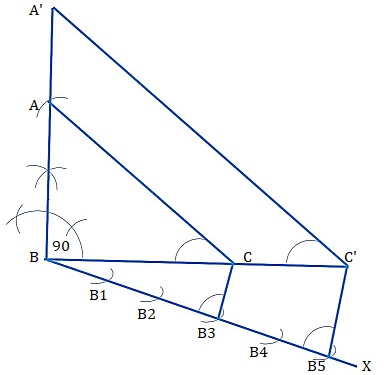
Draw a right triangle in which the sides (other than hypotenuse) are of lengths 4 cm and 3 cm. Then construct another triangle whose sides areAnswer
Step 1: Draw a line BC of 7cm
Step 2:At B draw ∠B =90
Step 3:B as center draw arc with 4 cm radius
Step 4:join AC
Step 5:ABC Triangle
Step 6: Draw a line BX with acute angle with BC .
Step 7: Mark 5 point B1, B2, B3, B4, on the line BX such that BB1 = B1B2 = B2B3= B3B4 = B4B5
Step 8: Join the points B3C.
Step 9: Draw a line from B5 parallel to B3C intersects the extended line BC at C’.
9. From C’, draw a line parallel to AC intersects the extended line AB at A’.
Chapter shortcuts
- Chapter 1 · Real Numbers
- Chapter 2 · Polynomials
- Chapter 3 · Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables
- Chapter 4 · Quadratic Equations
- Chapter 5 · Arithmetic Progressions
- Chapter 6 · Triangles
- Chapter 7 · Coordinate Geometry
- Chapter 8 · Introduction to Trigonometry
- Chapter 9 · Some Applications of Trigonometry
- Chapter 10 · Circles
- Chapter 11 · Constructions
- Chapter 12 · Area Related to Circles
- Chapter 13 · Surface Areas and Volumes
- Chapter 14 · Statistics
- Chapter 15 · Probability