Stay organised
Bookmark tricky questions or drop a doubt from the dashboard to revisit later.
Open dashboard →NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12 – Electricity and Circuits
Review every NCERT question with simple explanations and chapter diagrams.
Discover our NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12: Electricity and Circuits. This chapter introduces students to the basics of electricity, the components of electric circuits, and their functions. Our clear and detailed solutions help students understand how circuits work, including series and parallel connections. Perfect for exam preparation and reinforcing classroom learning, these answers make electrical concepts accessible and engaging.
Question 1
Fill in the blanks:(a) A device that is used to break an electric circuit is called a ______ __.
(b) An electric cell has ______ __ terminals.
Answer 1:
(a) A device that is used to break an electric circuit is called a switch .(b) An electric cell has two terminals.
Question 2
Mark ‘True’ or ‘False’ for the following statements:(a) Electric current can flow through metals.
(b) Instead of metal wires, a jute string can be used to make a circuit.
(c) Electric current can pass through a sheet of thermocol.
Answer 2:
Question 3
Explain why the bulb would not glow in the arrangement shown in Fig.12.13.
Answer 3:
In the given arrangement, the bulb would not glow because handle of screw is made of insulator which does not allow the flow of current.Question 4
Complete the drawing shown in Fig 12.14 to indicate where the free ends of the two wires should be joined to make the bulb glow.
Answer 4:
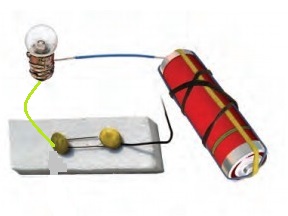
the free terminal of the cell should be connected to one end of the switch and the base terminal of the bulb should be connected to the other end of the switch .
Question 5
. What is the purpose of using an electric switch? Name some electrical gadgets that have switches built into them.Answer 5:
A switch is device that used to break or complete an electric circuit. electrical gadgets that have switches built into them are electric lamps, cooler, washing machines, table fan, TV, radio, etc.Question 6
. Would the bulb glow after completing the circuit shown in Fig. 12.14, if instead of safety pin we use an eraser?Answer 6:
If we complete the circuit given in Fig. 12.14 using an eraser then the bulb would not glow because eraser is a bad conductor of electricity. Hence, it will break the circuit.Question 7
. Would the bulb glow in the circuit shown in Fig. 12.15?
Answer 7:
we should make a correction as follow

Question 8
. Using the ‘conduction tester’ on an object, it was found that the bulb begins to glow. Is the object a conductor or an insulator? Explain.Answer 8:
Yes, the given object is a conductor as it allows the electric current to pass through it and make circuit complete and bulb of tester to glow. So object is conductorQuestion 9
. Why should an electrician use rubber gloves while repairing an electric switch at your home? Explain.Answer 9:
the rubber gloves will save the electrician from any electric shock while repairing an electric switch or appliance because rubber is a bad conductor of electricity so it does not allow the electric current to pass through it.Question 10
. The handles of tools like screwdrivers and pliers used by electricians for repair work usually have plastic or rubber covers on them. Can you explain why?Answer 9:
Plastic or rubber is an insulator which does not allow electric current to pass through it. The handles of tools like screwdrivers and pliers used by electricians for repair work usually have plastic or rubber cover on them so that they do not allow the current to pass through them and save the electrician from any electric shock.Our NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12 provide essential insights into electricity and circuits. Explore additional chapters and educational resources on our website to support your learning journey in science.
Chapter 1:Food Does It Come From
Chapter 4:Sorting Materials and Group
Chapter 5:Separation of substance
Chapter 7:Getting to know Plants
Chapter 9:The Living Oraganisms and Their Surroundings
Chapter 10:Motin and Measurement of Distances
Chapter 11:Light,Shadows and Reflections